
Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) Spacecraft Cruising to Mars
Guided by the stars, Curiosity has reached the halfway point of its interplanetary cruise phase from the Earth to Mars in between launch on Nov. 26, 2011 and final approach in August 2012. The spacecraft includes a disc-shaped solar powered cruise stage (on the left) attached to the aeroshell (right). Curiosity and the descent stage are tucked inside the aeroshell. Along the way to Mars, the cruise stage will perform six trajectory correction maneuvers (TCM’s) to adjust the spacecraft's path toward its final, precise landing site on Mars. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Guided by the stars, Curiosity has reached the halfway point of its interplanetary cruise phase from the Earth to Mars in between launch on Nov. 26, 2011 and final approach in August 2012. The spacecraft includes a disc-shaped solar powered cruise stage (on the left) attached to the aeroshell (right). Curiosity and the descent stage are tucked inside the aeroshell. Along the way to Mars, the cruise stage will perform six trajectory correction maneuvers (TCM’s) to adjust the spacecraft's path toward its final, precise landing site on Mars. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
As of today, NASA’s car sized Curiosity rover has reached the halfway point in her 352 million mile (567 million km) journey to Mars – No fooling on April 1, 2012.
Its T Minus 126 days until Curiosity smashes into the Martian atmosphere to brave the hellish “6 Minutes of Terror” – and, if all goes well, touch down inside Gale Crater at the foothills of a Martian mountain taller than the tallest in the continental United States – namely Mount Ranier.
Curiosity will search for the ingredients of life in the form of organic molecules – the carbon based molecules which are the building blocks of life as we know it. The one-ton behemoth is packed to the gills with 10 state of the art science instruments including a 7 foot long robotic arm, scoop, drill and laser rock zapper.
The Curiosity Mars Science laboratory (MSL) rover was launched from sunny Florida on Nov. 26, 2011 atop a powerful Atlas V rocket for an 8.5 month interplanetary cruise from the Earth toMars and is on course to land on the Red Planet early in the morning of Aug. 6, 2012 EDT and Universal Time (or Aug. 5 PDT).
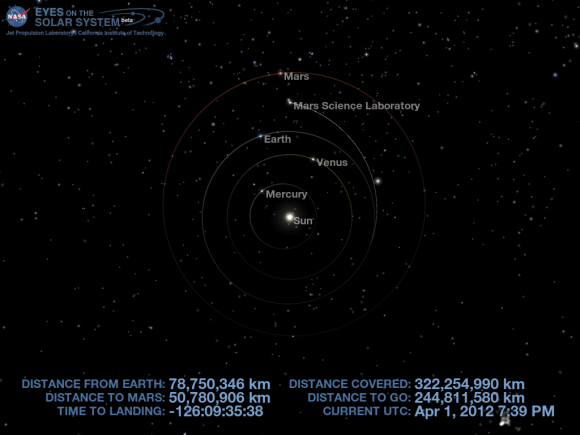
Curiosity’s Position in Space on April 1, 2012 - Halfway to Mars
This roadmap shows Curiosity's flight path through the Solar System - From Earth to Mars during the 8.5 month interplanetary cruise. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
This roadmap shows Curiosity's flight path through the Solar System - From Earth to Mars during the 8.5 month interplanetary cruise. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
On March 26, engineers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., successfully ignited the spacecrafts thrusters for the second of six planned trajectory correction maneuvers (TCM’s) to adjust the robots flight path during the long journey to achieve a pinpoint landing beside the Martian mountain.
“It is satisfying to get the second maneuver under our belts and know we are headed in the right direction,” said JPL’s Erisa Hines, systems lead for the maneuver. “The cruise system continues to perform very well.”
This maneuver was one-seventh as much as the flight’s first course adjustment, on Jan. 11. The cruise stage is equipped with eight thrusters grouped into two sets of four that fire as the entire spacecraft spins at two rotations per minute. The thruster firings change the velocity of the spacecraft in two ways – along the direction of the axis of rotation and also perpendicular to the axis. Altogether there were more than 60 pulsing maneuvers spaced about 10 seconds apart.
“The purpose is to put us on a trajectory to the point in the Mars atmosphere where we need to be for a safe and accurate landing,” said Mau Wong, maneuver analyst at JPL.

Atlas V rocket and Curiosity Mars rover poised at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral, Florida prior to Nov. 26, 2011 liftoff. Credit: Ken Kremer
Marking another crucial milestone, the flight team has also powered up and checked the status of all 10 MSL science instruments - and all are nominal.
“The types of testing varied by instrument, and the series as whole takes us past the important milestone of confirming that all the instruments survived launch,” said Betina Pavri of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., science payload test engineer for the mission. “These checkouts provide a valuable calibration and characterization opportunity for the instruments, including camera dark images and a measurement of zero pressure in the vacuum of space for the rover weather station’s pressure sensor.”
Ever since it was the first of MSL’s science instruments to be switched on three months ago, the Radiation Assessment Detector (RAD) has been collecting valuable measurements about the potentially lethal radiation environment in space and acting as a stunt double for determining the potential health effects on future human travelers to Mars.
RAD has been collecting data on the recent wave of extremely powerful solar flares erupting from the sun.
Curiosity has another 244 million kilometers to go over the next 4 months. .
All hopes ride on Curiosity as America’s third and last generation of Mars rovers.
Devastating funding cuts to NASA’s Planetary Science budget have forced NASA to cancel participation in the 2018 ExoMars lander mission that had been joint planned with ESA, the European Space Agency. ESA now plans to forge ahead with Russian participation.
Stay tuned
Source: Universe Today
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario